Elements compounds and mixtures quiz – Welcome to the Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Quiz, a comprehensive assessment designed to evaluate your understanding of these fundamental chemical concepts. This quiz will challenge you to identify, classify, and explain the properties and behaviors of elements, compounds, and mixtures, providing a deeper insight into the fascinating world of chemistry.
Throughout this quiz, you will encounter a series of questions that delve into the unique characteristics of each category. From the fundamental building blocks of matter to the intricate interactions between molecules, this quiz will test your knowledge and expand your understanding of the chemical world.
Elements: Elements Compounds And Mixtures Quiz
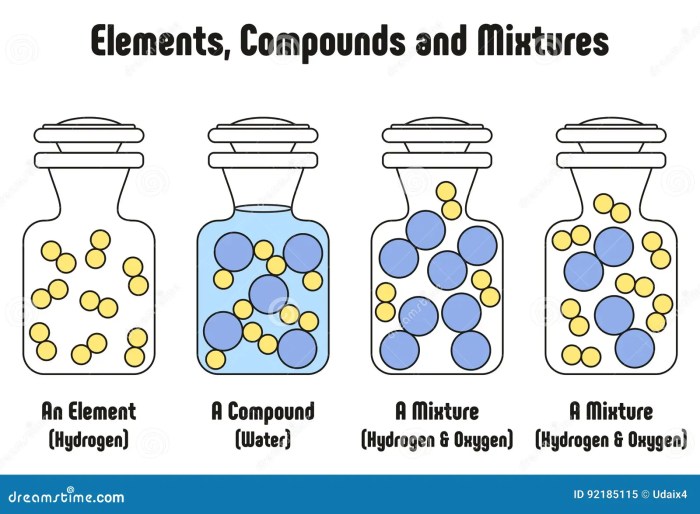
An element is a fundamental chemical substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Elements are the building blocks of all matter and are represented by the periodic table.
Properties of Elements
- Atomic number:The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element’s identity.
- Atomic mass:The average mass of an atom, considering its isotopes.
- Electronegativity:The ability of an atom to attract electrons.
- Reactivity:The tendency of an atom to undergo chemical reactions.
Role of Elements in Compounds and Mixtures
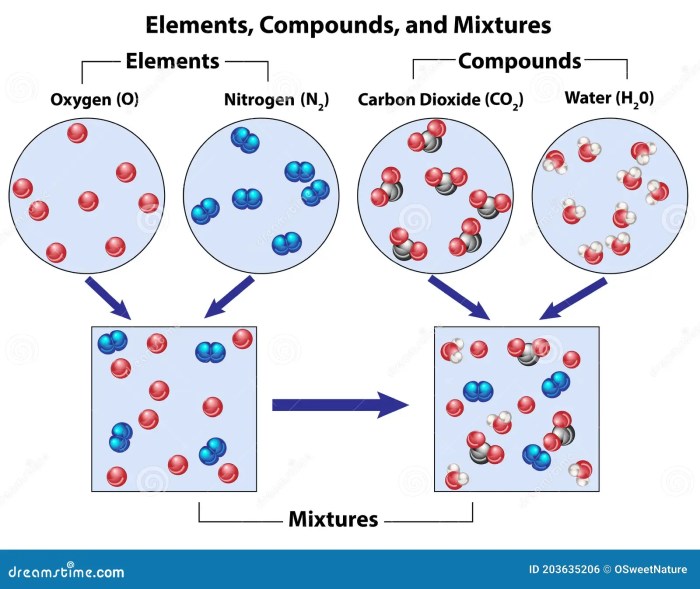
Elements can combine with each other to form compounds, which are substances with a fixed composition and distinct properties. In compounds, the elements are chemically bonded together and cannot be separated by physical means.
Elements can also be present in mixtures, which are combinations of substances that retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical means, such as filtration or distillation.
Compounds

A compound is a substance composed of two or more different elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. Compounds differ from elements in that elements are substances composed of only one type of atom, while compounds contain atoms of different elements bonded together.
Types of Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form compounds. There are several types of chemical bonds, including:
- Ionic bonds: Formed between a metal and a nonmetal, where one atom transfers electrons to the other, creating oppositely charged ions that attract each other.
- Covalent bonds: Formed when atoms share electrons to create a stable electron configuration.
- Metallic bonds: Formed between metal atoms, where the metal atoms share their valence electrons in a “sea” of electrons.
Examples of Compounds
Examples of compounds include:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl): An ionic compound formed between sodium and chlorine.
- Water (H2O) : A covalent compound formed between hydrogen and oxygen.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) : A covalent compound formed between carbon and oxygen.
Compounds have unique properties that differ from their constituent elements. For instance, sodium chloride is a solid with a high melting point, while sodium is a soft, silvery metal, and chlorine is a toxic gas.
Mixtures
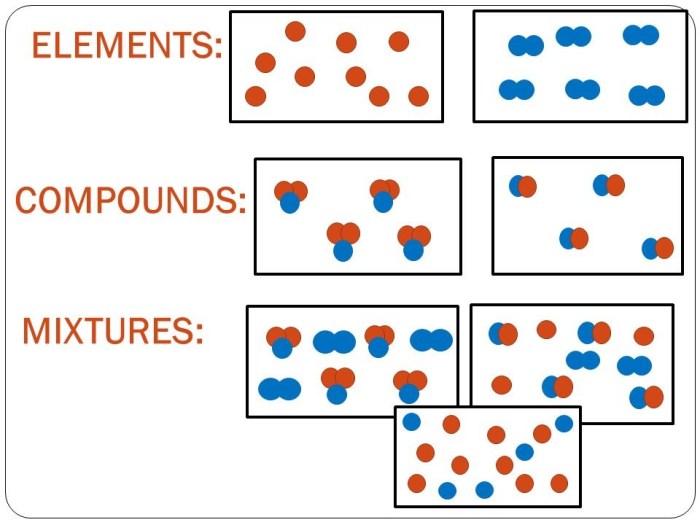
A mixture is a combination of two or more chemical substances that are not chemically bonded. The substances retain their identity and are mixed in different forms, for example, solutions, suspensions, or colloids. Mixtures are created by mechanically blending or mixing elements and compounds without any chemical bonding or change in their composition.
Unlike compounds, mixtures can be easily separated into their constituent elements or compounds using physical methods like filtration, distillation, or chromatography. The composition of a mixture can vary, and the proportions of its components can be adjusted without altering the properties of the individual substances.
Types of Mixtures
Mixtures can be classified into two main types based on their physical appearance and the distribution of their components:
- Homogeneous Mixtures:Homogeneous mixtures are uniform throughout, meaning their components are evenly distributed and cannot be distinguished from one another. They appear as a single phase and have consistent properties throughout. Examples of homogeneous mixtures include saltwater, air, and alloys.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures:Heterogeneous mixtures are non-uniform and consist of visibly different components. The components may be present in different phases, such as solid, liquid, or gas. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include sand in water, oil in water, and granite.
Quiz
The quiz is designed to assess students’ understanding of the concepts of elements, compounds, and mixtures. It includes questions that require students to identify, classify, and explain these concepts.
Questions
- Define an element and provide an example.
- Define a compound and provide an example.
- Define a mixture and provide an example.
- Classify the following substances as elements, compounds, or mixtures:
- Water
- Gold
- Salt
- Air
- Explain the difference between a homogeneous mixture and a heterogeneous mixture.
- Describe a method for separating a mixture of sand and water.
Answer Key, Elements compounds and mixtures quiz
1. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Example
gold.
2. A compound is a pure substance that is made up of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. Example
water.
3. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. Example
air.
4.
Water
compound
Gold
element
Salt
compound
Air
mixture
- A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture.
- A mixture of sand and water can be separated by filtration. The sand will be retained on the filter paper, while the water will pass through the filter paper.
FAQs
What is the primary distinction between an element and a compound?
An element is a pure substance composed of only one type of atom, while a compound is a substance composed of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together.
Can a mixture be separated into its constituent elements or compounds?
Yes, a mixture can be separated into its constituent elements or compounds using physical methods such as filtration, distillation, or chromatography.
What type of chemical bond is responsible for holding atoms together in a compound?
Covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds are the primary types of chemical bonds that hold atoms together in a compound.