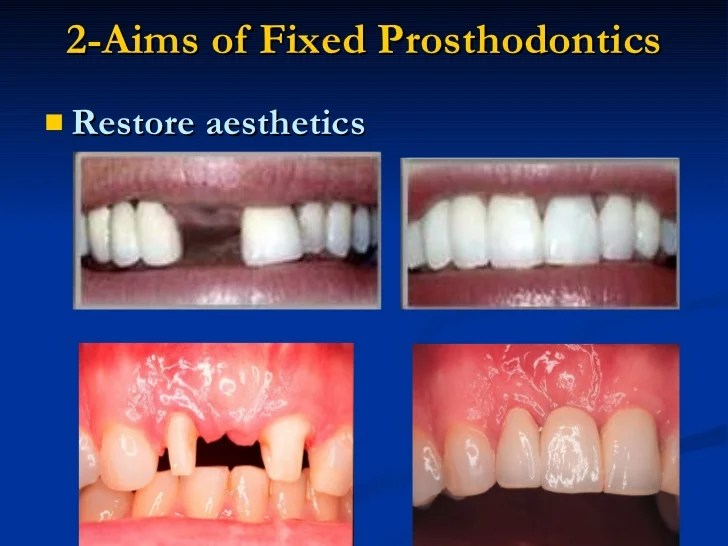
Fixed prosthodontics is commonly referred to as – Fixed prosthodontics, commonly referred to as crowns, bridges, and veneers, has revolutionized the field of dentistry. These dental restorations offer a myriad of benefits, ranging from restoring function to enhancing aesthetics. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of fixed prosthodontics, exploring its types, indications, design principles, fabrication process, clinical considerations, and future directions.
With a focus on precision and durability, fixed prosthodontics has become an indispensable tool for dentists seeking to restore the health and beauty of their patients’ smiles.
Types of Fixed Prosthodontics: Fixed Prosthodontics Is Commonly Referred To As
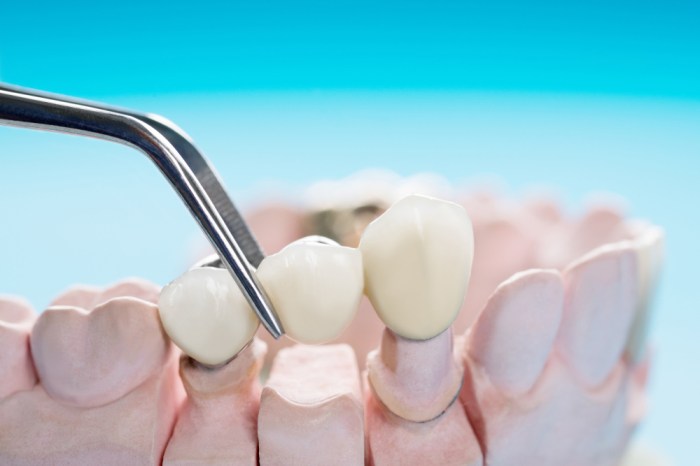
Fixed prosthodontics encompasses various types of dental restorations that are permanently attached to the teeth or supporting structures. These restorations serve to replace missing teeth, restore damaged teeth, or improve aesthetics. The following table provides an overview of different types of fixed prosthodontics, their characteristics, and their clinical applications:
| Type | Material | Design | Indications | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crowns | Ceramic, metal, zirconia | Covers the entire visible portion of the tooth | – Restore severely damaged or weakened teeth
|
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
| Bridges | Ceramic, metal, zirconia | Replaces one or more missing teeth by connecting to adjacent teeth | – Restore missing teeth
|
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
| Veneers | Ceramic, composite resin | Thin shells that are bonded to the front surface of teeth | – Improve aesthetics by correcting shape, color, or size of teeth
|
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
| Inlays and Onlays | Ceramic, metal, zirconia | Restore a portion of a tooth, either within the cusp (inlay) or extending over the cusp (onlay) | – Restore damaged teeth that are not severely compromised
|
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
| Implants | Titanium | Artificial tooth root surgically placed into the jawbone | – Replace missing teeth without affecting adjacent teeth
|
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
|
FAQ Insights
What are the different types of fixed prosthodontics?
Fixed prosthodontics encompasses a range of restorations, including crowns, bridges, and veneers. Each type serves a specific purpose, from restoring a single damaged tooth to replacing multiple missing teeth.
When is fixed prosthodontics recommended?
Fixed prosthodontics is commonly recommended in cases of tooth decay, fracture, or missing teeth. It can also be used to improve the aesthetics of a smile or correct bite problems.
What are the advantages of fixed prosthodontics?
Fixed prosthodontics offers numerous advantages, including improved function, enhanced aesthetics, increased durability, and protection of the remaining teeth.