Welcome to the fascinating world of orchestral music, where young person’s guide to the orchestra worksheet embarks on a journey to unravel the captivating tapestry of instruments, conductors, and musical masterpieces. Delve into the intricacies of each section, from the soaring strings to the resonant brass, and discover the harmonious blend that creates an unforgettable symphony of sound.
Prepare to be enthralled as we explore the instruments of the orchestra, their unique timbres, and the renowned composers who have harnessed their power. Witness the maestro’s baton guide the musicians in a seamless performance, showcasing the collaborative nature of orchestral music.
Introduction to the Orchestra
An orchestra is a large ensemble of musicians playing a variety of musical instruments. The primary purpose of an orchestra is to perform classical music, which encompasses a wide range of genres and styles from the Baroque period to the present day.
Orchestras are typically divided into four main sections: strings, woodwinds, brass, and percussion. Each section consists of a group of instruments that share similar characteristics in terms of their sound and playing techniques.
The development of the orchestra has evolved over several centuries, with significant advancements during the Baroque and Classical periods. The modern symphony orchestra as we know it today emerged in the 19th century, featuring a standardized instrumentation and seating arrangement.
The Instruments of the Orchestra

Strings
The string section is the largest section of the orchestra, typically consisting of violins, violas, cellos, and double basses. String instruments produce sound by vibrating strings with a bow or by plucking them with the fingers.
Famous Composers for Strings:
- Antonio Vivaldi (violin concertos)
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (string quartets)
- Ludwig van Beethoven (string symphonies)
Woodwinds
The woodwind section includes instruments such as flutes, oboes, clarinets, and bassoons. Woodwind instruments produce sound by blowing air across a reed or mouthpiece.
Famous Composers for Woodwinds:
- Claude Debussy (flute)
- Richard Strauss (oboe)
- Igor Stravinsky (clarinet)
Brass
The brass section consists of instruments such as trumpets, trombones, French horns, and tubas. Brass instruments produce sound by vibrating their lips into a mouthpiece.
Famous Composers for Brass:
- Gustav Holst (trombone)
- Aaron Copland (trumpet)
- Richard Wagner (French horn)
Percussion
The percussion section includes a wide range of instruments, such as drums, cymbals, and xylophones. Percussion instruments produce sound by striking, shaking, or scraping them.
Famous Composers for Percussion:
- Carl Orff (xylophone)
- Béla Bartók (drum)
- Leonard Bernstein (cymbals)
How an Orchestra Works
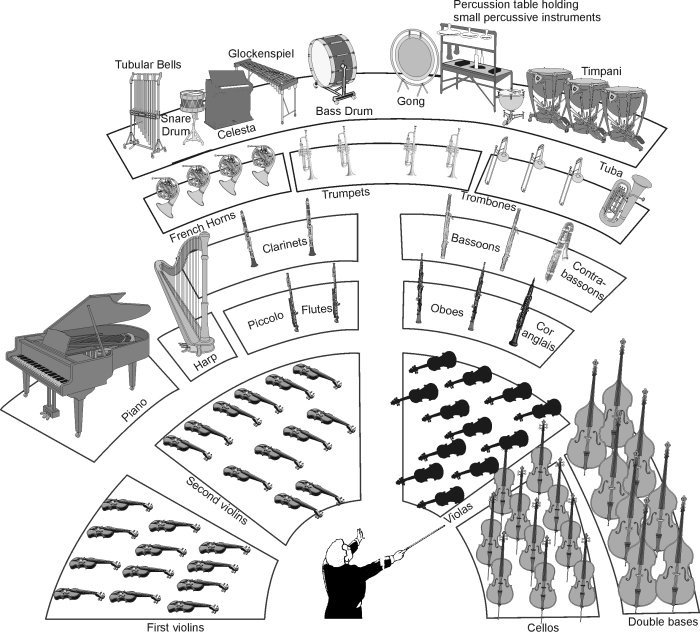
The Role of the Conductor
The conductor is the leader of the orchestra and is responsible for coordinating the performance of all the musicians. The conductor uses gestures and cues to indicate the tempo, dynamics, and phrasing of the music.
Collaboration and Cohesion
Musicians in an orchestra work together to create a cohesive sound. They must listen attentively to each other and adjust their playing accordingly. Rehearsals are essential for developing this level of coordination.
Importance of Rehearsal and Practice
Rehearsal and practice are crucial for the success of an orchestral performance. They allow musicians to refine their technique, improve their ensemble skills, and develop a shared interpretation of the music.
Listening to an Orchestra
Tips for Effective Listening
To fully appreciate an orchestral performance, it is important to listen attentively and engage with the music. Pay attention to the melody, harmony, rhythm, and dynamics of the music.
Musical Elements to Pay Attention To
Key musical elements to pay attention to include:
- Melody:The main tune or theme of the music.
- Harmony:The combination of notes played together to create chords.
- Rhythm:The pattern of beats and accents in the music.
- Dynamics:The volume and intensity of the music.
Emotional Impact of Orchestral Music
Orchestral music can convey a wide range of emotions and ideas. It can evoke feelings of joy, sadness, excitement, and awe. Composers use various musical techniques to create these emotional effects.
Attending an Orchestra Concert: Young Person’s Guide To The Orchestra Worksheet
Concert Etiquette, Young person’s guide to the orchestra worksheet
Attending an orchestral concert requires certain etiquette. Be respectful of the musicians and other audience members by arriving on time, remaining quiet during the performance, and avoiding distractions.
Choosing a Seat and Dress Code
When choosing a seat, consider your budget and preferences. Different sections of the concert hall offer varying acoustic experiences. The dress code for orchestral concerts is typically formal or semi-formal.
Types of Orchestral Concerts
There are different types of orchestral concerts available:
- Symphony:A full orchestra performing a large-scale work, such as a symphony or concerto.
- Chamber:A smaller ensemble of musicians performing intimate works, such as chamber music.
- Opera:A theatrical performance that combines singing, acting, and orchestral accompaniment.
Careers in Orchestral Music

Career Paths
Musicians in an orchestra can pursue a variety of career paths. They may perform as soloists, chamber musicians, or orchestral players. Some may also become conductors or music educators.
Education and Training
Becoming a professional orchestral musician requires extensive education and training. Musicians typically begin their training at a young age and pursue degrees in music performance from prestigious music schools.
Successful Orchestral Musicians
Examples of successful orchestral musicians include:
- Yo-Yo Ma (cellist)
- Itzhak Perlman (violinist)
- Leonard Bernstein (conductor)
Question & Answer Hub
What is the role of the conductor in an orchestra?
The conductor leads the orchestra, setting the tempo, dynamics, and overall interpretation of the music.
How can I prepare for an orchestral concert?
Dress appropriately, arrive on time, and familiarize yourself with the program to enhance your listening experience.
What are the different types of orchestral concerts?
Symphony concerts feature a full orchestra, chamber concerts showcase smaller ensembles, and opera combines music with drama.