Classical conditioning vs operant conditioning worksheet – Embark on an educational journey with our “Classical Conditioning vs. Operant Conditioning Worksheet,” a comprehensive guide that delves into the intricacies of these two fundamental learning processes. Through engaging examples and expert insights, this worksheet unravels the mechanisms of classical and operant conditioning, empowering you with a deeper understanding of how behavior is shaped.
Classical Conditioning
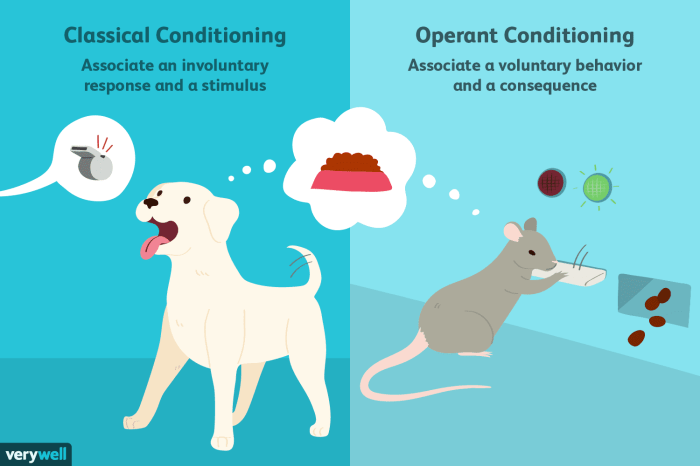
Classical conditioning, also known as Pavlovian conditioning, is a type of learning in which a neutral stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response. The unconditioned stimulus is a naturally occurring stimulus that triggers an automatic response, while the neutral stimulus is a previously neutral stimulus that, after pairing with the unconditioned stimulus, eventually elicits the same response.
Key Concepts, Classical conditioning vs operant conditioning worksheet
- Unconditioned stimulus (US):A stimulus that naturally triggers a response.
- Unconditioned response (UR):The natural response elicited by the unconditioned stimulus.
- Conditioned stimulus (CS):A previously neutral stimulus that, after pairing with the unconditioned stimulus, elicits a conditioned response.
- Conditioned response (CR):The learned response elicited by the conditioned stimulus.
Classical conditioning plays a significant role in everyday life, shaping our responses to various stimuli. For instance, the sound of a bell can become a conditioned stimulus for salivation if it is repeatedly paired with the presentation of food (unconditioned stimulus).
Operant Conditioning
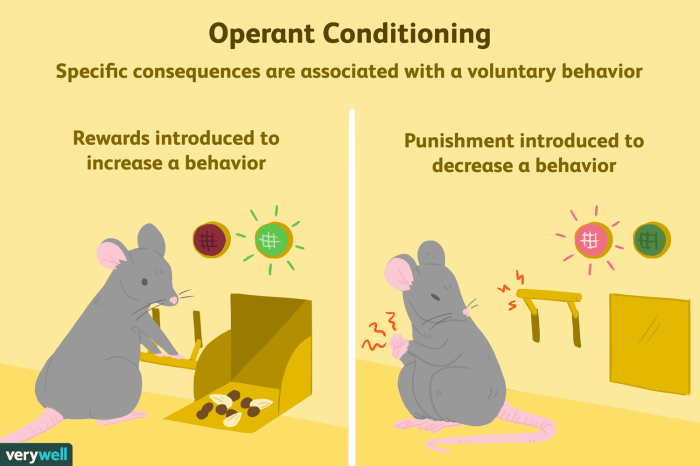
Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a type of learning in which the consequences of a behavior determine the likelihood of that behavior being repeated. Reinforcement, a positive consequence, increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated, while punishment, a negative consequence, decreases the likelihood.
Key Concepts, Classical conditioning vs operant conditioning worksheet
- Reinforcement:Any consequence that increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
- Positive reinforcement:A pleasant consequence that follows a behavior, increasing its likelihood of repetition.
- Negative reinforcement:An unpleasant consequence that is removed after a behavior, increasing its likelihood of repetition.
- Punishment:Any consequence that decreases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated.
- Positive punishment:An unpleasant consequence that follows a behavior, decreasing its likelihood of repetition.
- Negative punishment:A pleasant consequence that is removed after a behavior, decreasing its likelihood of repetition.
Operant conditioning is widely used in everyday life, such as in animal training, child rearing, and education. For instance, rewarding a dog with a treat for sitting (reinforcement) increases the likelihood of the dog repeating the behavior.
Comparison of Classical and Operant Conditioning
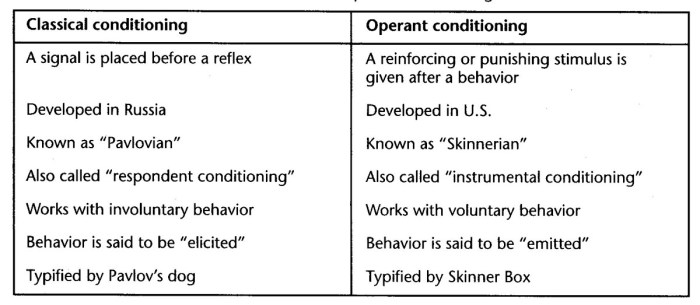
| Feature | Classical Conditioning | Operant Conditioning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through association of stimuli | Learning through consequences of behavior |
| Key Concepts | US, UR, CS, CR | Reinforcement, punishment |
| Examples | Salivating at the sound of a bell | Getting a treat for sitting |
Classical conditioning focuses on the association between stimuli, while operant conditioning emphasizes the consequences of behavior. Classical conditioning typically involves involuntary responses, whereas operant conditioning involves voluntary behaviors.
Applications of Classical and Operant Conditioning

Classical and operant conditioning have numerous practical applications, including:
- Education:Classical conditioning can be used to teach associations, such as pairing a word with an image. Operant conditioning can be used to reinforce desired behaviors in students.
- Psychology:Classical conditioning is used in therapies like exposure therapy to reduce anxiety. Operant conditioning is used in behavior modification programs to change maladaptive behaviors.
- Animal training:Both classical and operant conditioning are used to train animals, from teaching dogs to sit to training dolphins to perform tricks.
Ethical considerations should be taken into account when using these conditioning techniques, ensuring they are applied responsibly and with the well-being of individuals in mind.
User Queries: Classical Conditioning Vs Operant Conditioning Worksheet
What is the key difference between classical and operant conditioning?
Classical conditioning involves pairing a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus, while operant conditioning focuses on the consequences of behavior.
Can classical conditioning be used to treat phobias?
Yes, a technique called systematic desensitization uses classical conditioning principles to gradually reduce fear responses.
How does operant conditioning contribute to animal training?
Operant conditioning allows trainers to shape animal behavior by rewarding desired actions and ignoring or punishing unwanted ones.



