Carbon cycle fill in the blank diagram – Delving into the intricate workings of the carbon cycle, this comprehensive guide empowers readers with an authoritative understanding of its significance. Through an engaging narrative, we embark on a journey to uncover the processes, reservoirs, and human impacts that shape this fundamental cycle, unraveling its profound influence on Earth’s habitability.
The carbon cycle fill-in-the-blank diagram serves as a visual representation of this dynamic system, inviting readers to actively participate in understanding the flow of carbon between Earth’s major reservoirs. By filling in the blanks, learners gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of life and the delicate balance that sustains our planet.
Overview of the Carbon Cycle
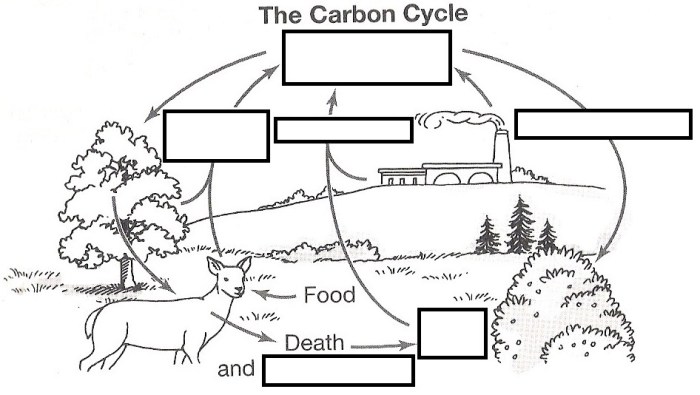
The carbon cycle is a complex and interconnected system of processes that describes the movement of carbon through the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, land biosphere, and geosphere. It plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate and supporting life as we know it.
The discovery and understanding of the carbon cycle have evolved over time, with significant contributions from scientists such as Antoine Lavoisier and Joseph Priestley in the 18th century. Today, the carbon cycle is widely recognized as a fundamental component of Earth’s biogeochemical processes.
Processes Involved in the Carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and certain bacteria convert carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere into organic compounds, using sunlight as energy. This process releases oxygen (O2) as a byproduct.
Respiration, Carbon cycle fill in the blank diagram
Respiration is the process by which living organisms use oxygen to break down organic compounds, releasing CO2 and energy. This process occurs in all living cells, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Decomposition
Decomposition is the process by which organic matter from dead organisms is broken down by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. This process releases CO2 and other nutrients back into the environment.
Combustion
Combustion is the process of burning organic matter, such as fossil fuels, wood, and biomass. This process releases CO2 and other pollutants into the atmosphere.
Carbon Reservoirs
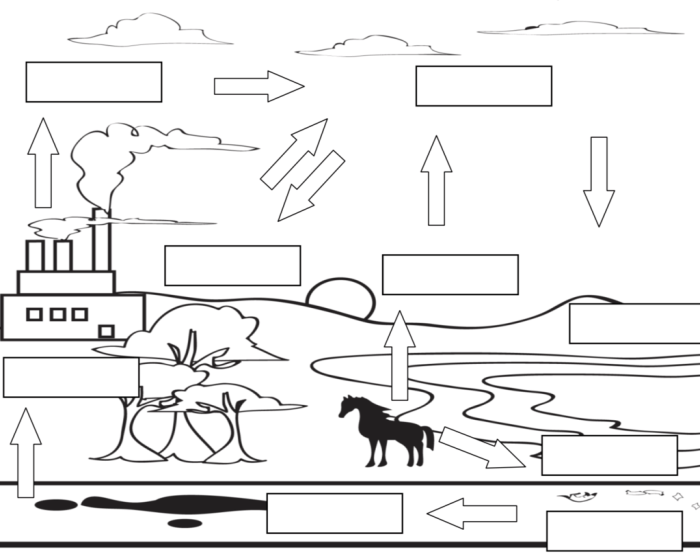
The major carbon reservoirs on Earth include:
- Atmosphere: Contains a relatively small amount of carbon in the form of CO2 and other carbon-containing gases.
- Oceans: Hold a significant amount of carbon dissolved in seawater and stored in marine organisms and sediments.
- Land Biosphere: Includes carbon stored in living plants, animals, and soils.
- Fossil Fuels: Contain vast amounts of carbon that have been stored underground for millions of years.
Anthropogenic Impacts on the Carbon Cycle: Carbon Cycle Fill In The Blank Diagram
Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, have significantly altered the carbon cycle. These activities release large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, leading to an increase in atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
The consequences of these impacts include climate change, ocean acidification, and changes in plant and animal life.
Importance of the Carbon Cycle
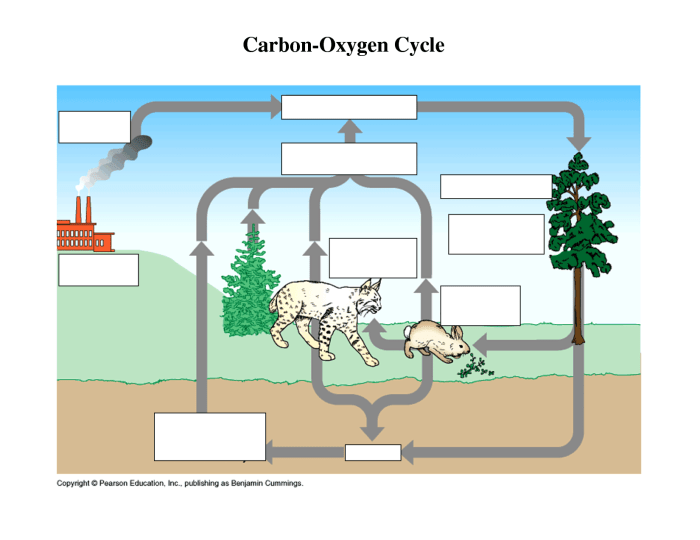
The carbon cycle plays a crucial role in maintaining Earth’s habitability by:
- Regulating atmospheric CO2 levels, which influences global climate.
- Providing essential nutrients for plants and other organisms.
- Storing carbon in long-term reservoirs, such as fossil fuels and deep-sea sediments.
General Inquiries
What is the significance of the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle plays a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate by absorbing and releasing carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas. It also provides the foundation for life on Earth, as carbon is a key component of all living organisms.
How do human activities affect the carbon cycle?
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, disrupting the natural balance of the carbon cycle. This can lead to climate change and other environmental problems.
What can be done to mitigate the impacts of human activities on the carbon cycle?
To mitigate the impacts of human activities on the carbon cycle, we need to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, invest in renewable energy sources, and protect and restore forests. These actions will help to reduce carbon emissions and maintain the balance of the carbon cycle.