Chapter 2 atoms molecules and ions answers to exercises – Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions – Exercises and Solutions delves into the fundamental building blocks of matter, providing a comprehensive understanding of their structure, properties, and interactions. This chapter serves as a gateway to unraveling the mysteries of chemistry and physics, laying the foundation for further exploration in these captivating fields.
Through a series of meticulously crafted exercises and their detailed solutions, this chapter empowers learners to grasp complex concepts with clarity and precision. It dispels common misconceptions and addresses challenges, fostering a deep understanding of the atomic and molecular realm.
Define Atoms, Molecules, and Ions: Chapter 2 Atoms Molecules And Ions Answers To Exercises
Atoms, molecules, and ions are the fundamental building blocks of matter. Understanding their structure and properties is essential for comprehending the behavior of substances and chemical reactions.
Atoms
Atoms are the smallest indivisible units of an element that retain the chemical properties of that element. They consist of a nucleus, which contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.
Molecules, Chapter 2 atoms molecules and ions answers to exercises
Molecules are neutral groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. The atoms in a molecule share electrons, forming covalent bonds. Molecules can be simple, such as hydrogen gas (H2), or complex, such as proteins and DNA.
Ions
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge. Positively charged ions are called cations, while negatively charged ions are called anions. Ions are formed when atoms undergo chemical reactions and transfer electrons to or from other atoms.
Exercises and Solutions

Exercises
- Define the term “atom” and describe its structure.
- Explain the difference between a molecule and an ion.
- Draw the Lewis structure of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Solutions
- An atom is the smallest indivisible unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. It consists of a nucleus, which contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.
- A molecule is a neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds, while an ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge.
- The Lewis structure of carbon dioxide (CO2) is:“`O=C=O“`
Applications of Atomic and Molecular Theory
The understanding of atoms and molecules has revolutionized our understanding of the world around us. This knowledge is applied in various fields, including:
Chemistry
Atomic and molecular theory provides the foundation for understanding chemical reactions and the properties of substances. It enables chemists to predict the behavior of elements and compounds, design new materials, and develop new drugs.
Physics
Atomic and molecular theory plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of matter at the atomic and molecular level. It helps physicists study the properties of solids, liquids, and gases, as well as the interactions between particles.
Other Disciplines
Atomic and molecular theory also has applications in other disciplines, such as biology, materials science, and environmental science. It provides insights into the structure and function of biological molecules, the properties of materials, and the behavior of pollutants in the environment.
Interactive Table of Elements
| Atomic Number | Symbol | Name | Group/Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | 1/1 |
| 2 | He | Helium | 18/1 |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | 1/2 |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | 2/2 |
| 5 | B | Boron | 13/2 |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 14/2 |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | 15/2 |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | 16/2 |
Molecular Models
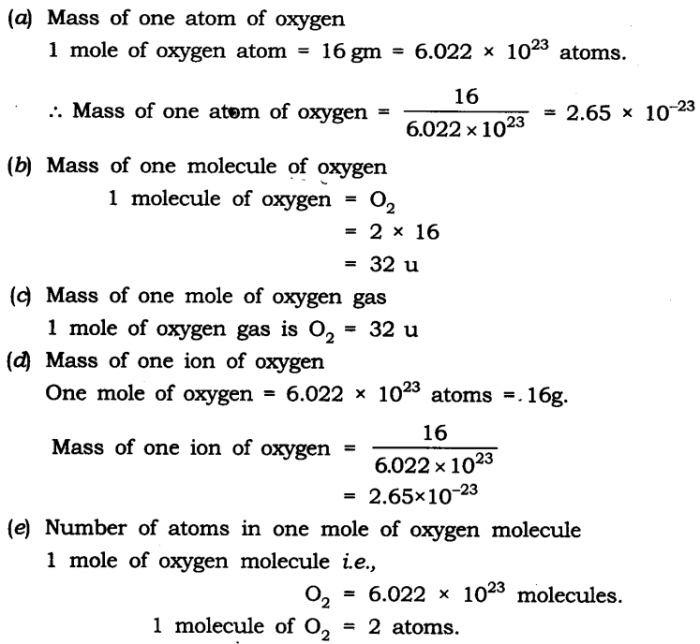
Molecular models are representations of the three-dimensional structure of molecules. They help scientists visualize and understand the arrangement of atoms within a molecule.
Types of Molecular Models
- Ball-and-stick models:Represent atoms as spheres and bonds as sticks.
- Space-filling models:Show the relative sizes and shapes of atoms, with atoms represented as spheres that touch each other.
- Electron density models:Depict the distribution of electrons around the molecule.
Advantages and Limitations
- Ball-and-stick models:Simple and easy to construct, but do not provide information about atomic sizes or electron density.
- Space-filling models:Show atomic sizes and shapes, but can be difficult to interpret.
- Electron density models:Provide detailed information about electron distribution, but are complex and difficult to construct.
Case Studies: Ions in Biological Systems
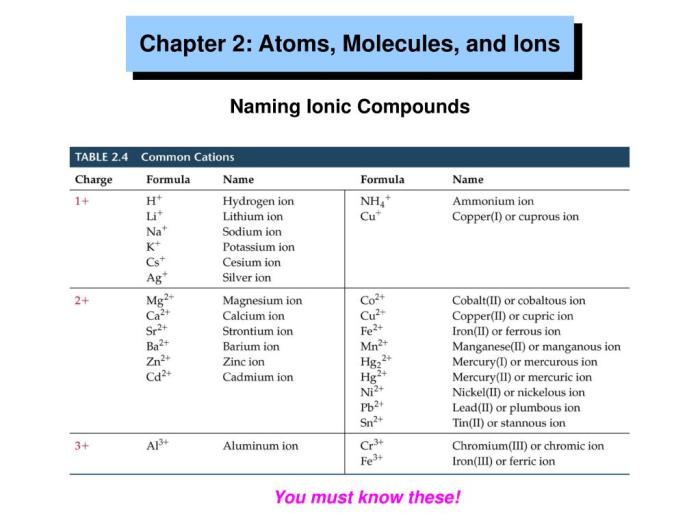
Ions play a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
Nerve Transmission
Ions, such as sodium and potassium, are responsible for the electrical impulses that transmit signals along nerves.
Muscle Contraction
Calcium ions are involved in the process of muscle contraction, triggering the release of energy that causes muscles to shorten.
Imbalances in Ion Levels
Imbalances in ion concentrations can lead to health problems, such as muscle cramps, arrhythmias, and seizures.
General Inquiries
What is the difference between an atom and a molecule?
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical identity, while a molecule is a group of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
What are the three types of ions?
Cations, anions, and zwitterions
What is the significance of atomic and molecular theory?
It provides the foundation for understanding the structure and behavior of matter, enabling advancements in various scientific fields.